Forex Trading is regulated in South Africa by the Financial Sector Conduct Authority (FSCA). The Financial Sector Conduct Authority (FSCA) is the statutory regulatory body that oversees financial markets including the forex market in South Africa. They also issue licenses to market participants like the forex brokers that accept retail traders.
For ensuring that your funds are safe, traders in South Africa must only trade via FSCA regulated CFD & forex brokers.
Steps to start Forex Trading for beginner traders in South Africa
Below are some of the points that you need to know for learning everything about forex trading:
- Forex Market Definition
- Currency Pairs
- Forex Trading Terminology
- How to Open Forex Trading Account
- Risks Involved in Forex Trading
- Learn how to Analyze the Forex Market
Also, it is important to understand that forex & CFD trading is very risky, and almost 70-80% of retail traders lose their money when trading at different CFD brokers in South Africa. Hence, if you are thinking about trading forex, then you must learn about the risks as well.
Show More
Summary & Comparison of Best Forex Trading Platforms in South Africa
| Broker |
Regulations |
EUR/USD Spread (pips) |
Min. Deposit |
Visit |
|
|
FSCA, FCA, CySEC
|
1.2
|
R100
|
Visit Broker
|
|
|
FSCA, FSA, FSC, ASIC
|
0.9
|
R1,750
|
Visit Broker
|
|
|
FSCA, CySEC, FCA, FSA
|
0.1
|
$100
|
Visit Broker
|
|
|
FSCA, FCA, CySEC
|
1.9
|
R20
|
Visit Broker
|

Plus500
|
FSCA, FCA, ASIC, CySEC
|
0.8
|
R1,500
|
Visit Broker
|
|
|
FSCA, FCA, CySEC
|
1
|
$10
|
Visit Broker
|
Note: The spread data on minimum deposit is the typical/minimum spread as per information on these brokers’ websites in October 2023.
Forex Market Definition
The foreign exchange market alias forex or FX market is a global, online over-the-counter (OTC) market where currencies of about 170 countries are bought and sold. It is open 24 hours a day. It is the biggest financial market in the world and has very high liquidity.
According to the Bank of International Settlement (BIS) survey conducted every three years, South Africa accounts for about 0.3% of forex turnover globally. The forex market participants include businesses, banks, speculators, institutions, etc.
Most of the trading is from banks, businesses & institutional investors. Some of the trades in the forex market are speculative in nature, and a part of them is from retail traders. Retail traders come to the forex market to speculate, hedge against currency and interest rate risk, etc.
The activities that take place in the forex market are what determine the exchange rate of any currency pair. The higher the demand for a currency, the higher its exchange rate.
Forex market participants
The forex market ecosystem teems with a lot of participants. Let us discuss some of them.
1) The Forex Broker
The forex broker is a regulated participant who acts as a bridge between the forex trader and the market.
The broker is a middleman who places buy and sell orders for retail traders and some brokers also offer research services as well if required by the trader. The forex broker charges a fee for their services.
That being said, retail traders need to pass through a forex broker that accepts retail traders if they are to access the market. There are several forex brokers in South Africa to choose from.
However, traders in South Africa should check the FSCA website for a list of regulated forex brokers to avoid patronizing fraudulent/scam brokerages.
There are two types of brokers. They are classified based on their execution model. Here is the breakdown
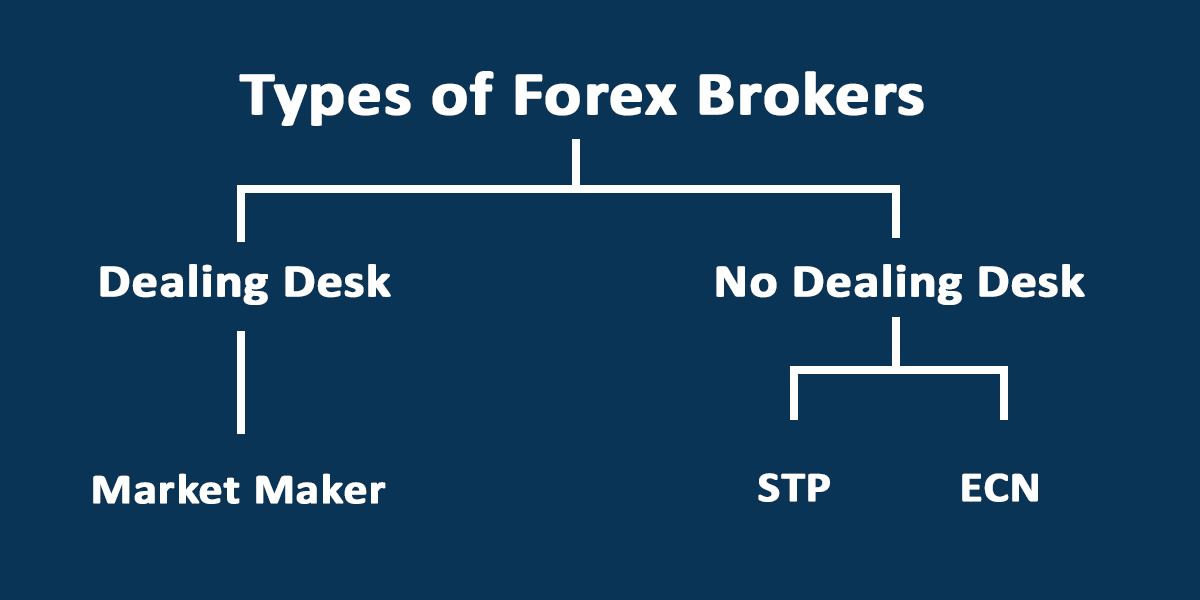
Dealing Desk Broker: Dealing desk brokers take the opposite side of your trades. When you buy a currency pair, they sell. When you sell, they buy. Because of this, when you lose a trade, they make money off it, leading to a conflict of interest. This is why traders tend to prefer non-dealing desk brokers.
Dealing Desk brokers are also known as market makers.
Non-dealing Desk (NDD) Broker: NDD brokers do not take the opposite sides of your trades and they are divided into two. There are NDD brokers that use computerized networks to connect you to buyers/sellers in the market. This type is referred to as an ECN broker.
The second type is the STP brokers. They connect your trades to buyers/sellers via their liquidity pool.
2) The Retail Forex Trader
Retail forex traders are individual investors who wish to trade in the forex market for personal gain. They don’t trade on behalf of an organization or company. They account for an estimated 5.5% of the global forex market as per BIS data.
Retail traders are in the market mostly for speculative reasons. They hope to profit from differences in exchange rates between currencies. Retail forex traders, based on how long they trade could be a scalper, day trader, or a swing trader.
Based on analysis, a retail forex trader could be a technical, fundamental, or sentimental trader.
3) Central Banks
Their presence in the forex market is to create policies that can affect the currency, intervene and stabilize the currency through increasing or decreasing interest rates, performing Open market operations in some situations, etc.
Central banks can also devalue their currency to make exports of their country more competitive to international buyers. In short, the Central bank plays a major role in deciding the value of a currency.
4) Commercial Banks
Commercial Banks make up the interbank market where they trade forex with other banks in very large volumes. These volumes are large enough to dictate the bid and ask prices for any currency. They trade on behalf of themselves and their customers.
5) Multinationals
Big companies that operate in different parts of the world have to trade in the forex market to hedge risk and also for business purposes.
A company hoping to buy raw materials from another part of the world may need to convert its currency to be able to pay the supplier at the other end.
Big companies that have business operations in other parts of the world may also want to convert and repatriate their profits in a stronger currency to hedge against the risk of currency depreciation.
Forex Market Time Zones
The forex market operates in four different time zones:
- Sydney (10pm GMT to 7am GMT)
- Tokyo (11pm GMT to 8am GMT)
- London (7am GMT to 4pm GMT)
- New York (12pm GMT to 9pm GMT)
Depending on the currency that you want to trade, some sessions can be better than others. Most of the trading is carried out in the London & New York sessions.
The best time to trade the majors is when some of the major sessions overlap. At this time, market participation and liquidity are high, and spreads are at their lowest.
For example, the ideal time to trade the GBP/USD currency pair, is during the London & New York sessions, because at that time liquidity in the market is highest.
If you are trading JPY-based pairs, then you will also find liquidity during the Asian session.
Currency Pairs
All the countries participate in the forex market and their currencies are represented as three-letter codes.
However, we will focus on the popular currencies here. The popular currencies and their codes are listed below.
- U.S Dollar – USD
- Great Britain Pound- GBP
- Euro- EUR
- Japanese Yen- JPY
- Swiss Franc- CHF
Forex Currency Pairs
Forex currencies are traded in pairs written as Base Currency/Quote Currency – GBP/USD
Currency pairs could be major, minor, or exotic. Let us discuss them below.
1. Major currency pairs
The major currency pairs quote the USD alongside another major currency.
They usually have the USD on one side of the quote either as a base or quote currency. Examples in order of popularity are:
- EUR/USD
- USD/JPY
- GBP/USD
- USD/CHF
- AUD/USD
- USD/CAD
- NZD/USD
2. Minor Currency pairs
These are currency pairs of strong economies that do not contain the USD. Examples are
- EUR/GBP
- GBP/JPY
- GBP/CHF
- EUR/CHF
- EUR/JPY
- CHF/JPY
3. Exotic Currency pairs
These are currency pairs involving a major currency and a currency of a smaller economy. These smaller economies are often referred to as emerging economies. Examples are
- USD/SEK- USD/Swedish Krona
- USD/DKK- USD/Danish krone
- USD/ZAR- USD/South African Rand
- USD/KES- USD/Kenyan Shilling
- USD/NGN- USD/Nigerian Naira
Reading a Forex Quote
Forex currencies are traded in pairs written as Base Currency/Quote Currency i.e. GBP/USD. The base currency is usually on the left while the quote currency will be on the right. Here is an illustration below

When you go long (buy) on a currency pair, the base currency is being bought while the quote currency is being used to pay for the base currency. It is the other way round when you go short (sell) on a currency pair.
Currencies are always traded in pairs at an exchange rate. The exchange rate is how much of the quote currency is required to buy the base currency.
Assume the GBP/USD exchange rate = 1.2
This means that it will take $1.2 to buy one GBP and vice versa.
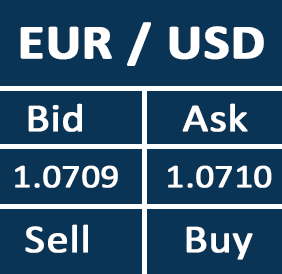
While trading forex, we use one currency to buy another hence we can also quote the currencies in terms of BID/ASK prices
The Bid price is the highest price a forex trader is willing to pay to buy the base currency from the broker.
The Ask price is the lowest price the forex broker is willing to sell the currency.
Forex Trading Terminology
Certain terms are widely used in forex trading and understanding is very important. We shall discuss some common terms below.
1) Spread
Spread is the difference between the bid price and the ask price of a currency pair.
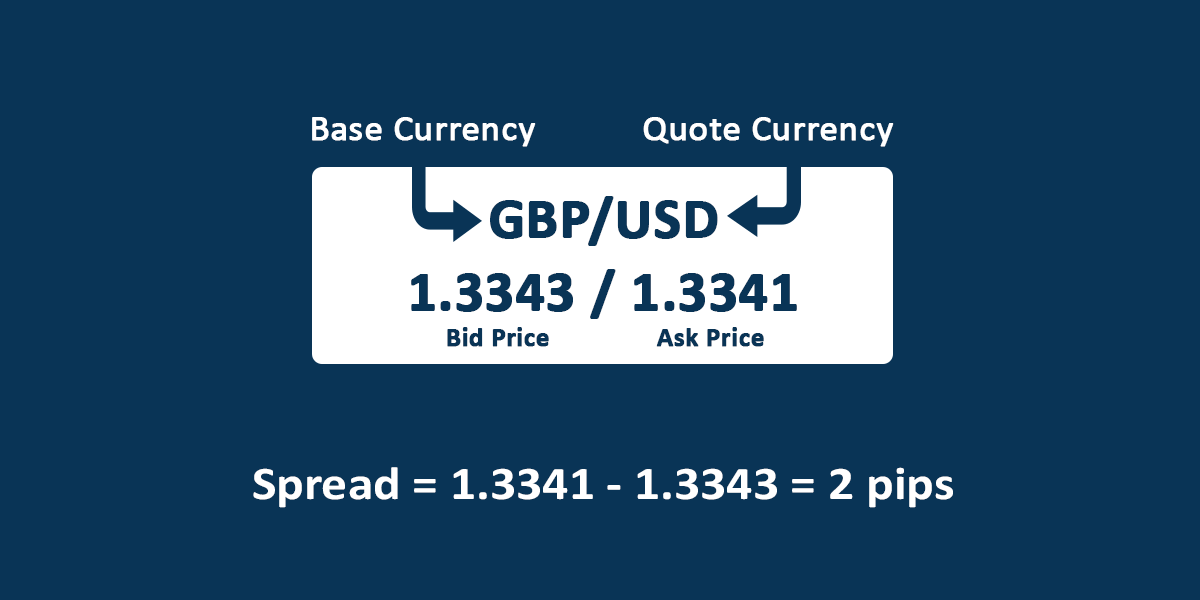
As seen in the image above the GBP/USD currency pair with a Bid/Ask price of 1.3089/1.3091 has a spread of 1.3089-1.3091 = 0.0002
Your forex broker may not always charge you a commission but makes their profit from the spread.
A spread of 0.0002 means if you are trading in a standard lot of 100,000 units of GBP/USD currency, the forex broker makes $20 on every standard lot traded i.e. 0.0002 x 100,000
There are two types of spreads in forex:
Variable spreads: As the name implies, variable spreads are spreads that fluctuate. This fluctuation is due to changes in the condition of the market like high or low volatility. This type of spread is usually offered by NDD brokers as they try to get the best market price for your trades.
Fixed Spreads:These are spreads that remain the same regardless of market conditions. They are usually offered by market makers. Market makers determine the price of the currency pairs they offer. So they can keep the bid and ask price stable no matter the market condition.
2) Pips
Percentage in point alias “pips” is the unit of measurement for the spread.
As seen in the example above, if the spread is 0.0002 it is conventionally expressed as 2 pips. This is for a currency up to the fourth decimal.
3) Lots
Forex currency pairs are traded in lots at forex brokers.
Since the currencies don’t move by a lot, the traders tend to trade a higher number of units. Remember, the higher the traded volume, the larger the profit & loss.
Currency pairs are divided into various lots as seen in the table below.
| Lot |
Number of units of currency |
| Standard |
100,000 |
| Mini |
10,000 |
| Micro |
1,000 |
Standard lot example:
For a GBP/USD currency pair with details below-
Exchange rate = $1.36
Standard lot = 100,000 units
The margin needed for trading 1 standard lot will be $136,000 (i.e., $1.36 x 100,000)
Mini lot example:
For a GBP/USD currency pair with details below-
Exchange rate = $1.36
Mini lot = 10,000 units
The balance required for trading a Mini lot will be $13,600 (i.e. $1.36 x 10,000)
So, the margin that you need to trade depends on the total lots or units that you are trading. If you are trading 2.5 Mini Lots, this means that you are trading 25,000 units of a currency.
4) Leverage
Leverage in forex trading is essentially taking a loan from your forex broker to trade most lots. The loan is repaid after you sell and make a profit or a loss.
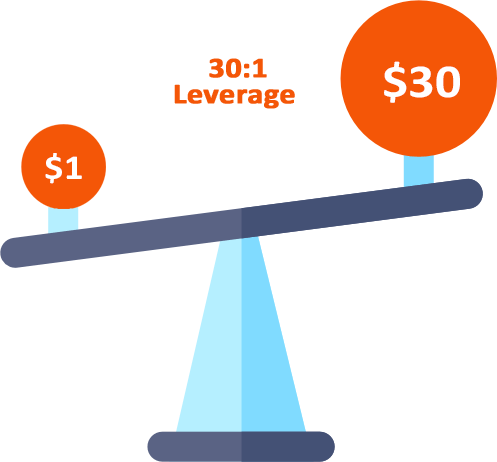
Most retail forex traders don’t have the required capital to buy or sell thousands of units of currency pair, so they leverage their position. But this is very risky and can result in huge losses.
Leverage of 30:1 means for every $1 a forex trader can trade up to a $30 position using margin money.
Leverage is inversely proportional to margin.
Example:
If margin is 3.33%, then leverage is 1/3.33 = 30 (also expressed as 1:30)
Since leveraging means taking a loan, it is a double-edged sword.
For example, if you lose big on a trade, and if the forex broker does not have Negative balance protection in place, the trader may have to repay more than the initial capital if the losses exceed capital.
The leverage that brokers can offer to retail traders in South Africa for CFDs & forex is as high as 1:1000 (depending on the instrument). This leverage is high and we advise you to choose much lower leverage to reduce the risk of huge losses.
5) Margin
This is a good faith deposit a trader must keep in his trading account. It is expressed as a percentage and is inversely proportional to leverage.
Margin % = 1/Leverage
For leverage of 30:1, the margin is 1/30 = 3.33%
Example:
If a forex trader uses leverage to place a buy order of 1 standard lot of GBP/USD currency pair
GBP/USD Exchange rate = $1.33
Margin = 3%
Required deposit without margin = $133,000 (i.e. 100,000 units x $1.33)
Required deposit with 3.33% margin= $4428.9 (i.e. 3.33% of $133,000)
After the forex trader deposits $4,428.9 in his or her account, then the 1 standard lot trade on GBP/USD can be placed.
6) Negative Balance Protection
This is a system put in place by forex brokers to ensure your account doesn’t go into negative when the market moves against you quickly.
Once you lose the deposits in your CFD trading account, the brokerage system automatically closes all your positions.
It limits your loss to just your capital and ensures that the forex broker does not take the risk of your position. Negative balance protection is offered to only retail traders and not institutional traders.
7) CFDs
CFDs (Contract For Differences) are derivatives, and these are contracts between the broker & trader. Derivatives are complex financial instruments that derive their value from other underlying asset such as Stock, Currency, and Commodities like Gold, precious metals, etc.
When trading CFDs, a trader does not own the underlying asset and is only speculating on the price of the instrument.
8) Hedging
This is the act of managing risk.
Traders sometimes trade derivative instruments such as currency futures and currency options to hedge against currency and interest rate fluctuation risk.
9) Day Trader
This is a trader who opens and closes trading positions on the same day.
Day traders are usually speculators and use derivative products like CFDs to try to profit from the rise or fall of the price of an asset.
10) Scalping
Scalping is a trading strategy that involves extreme short-term trading. Scalpers usually open and close their trades within a short time frame so they can profit from quick price movements.
11) Swing Trading
Swing trading is a long-term trading strategy. Swing traders combine fundamental and technical analysis before opening a trading position. They can hold their trade for some days. Some can even keep positions open for months.
12) Slippage
Slippage is the difference between the requested price of your order and the price it is executed by your broker. Slippage is can be caused by poor internet connection on your end, rapid price movement in the market, or your broker’s system. To know how your broker handles slippage, make sure you read their rider execution policy and other related official documents. They are usually available on the broker’s websites.
13) Forex Orders
A forex order is simply how you enter and exit the market. They are the offers you send to your broker from trading platforms. There are different types of orders you can place in the market. Here are the common ones:
Buy Order: This involves placing an order to purchase a currency pair. This order is instant. However, it has two variations called the buy stop and buy limit orders. A buy stop is when you set your entry price above the current market price. If the price rises to the level you have set, your buy order is triggered.
On the other hand, a buy limit means setting your entry price below the current market price in hope that the price will fall to that level. If it does, your buy order will be triggered.
Sell Order: It involves placing a trade to short (sell) a currency pair. A sell order is instant but has two variations too – the sell stop and sell limit orders. For a sell stop, you place your order at a price below the market price with the hope that the price will fall further from that point. If the price falls to the point you have set, your sell order will be activated.
For the sell limit, you place your sell order at an entry price above the current price, with the hope that the price will fall from there. If the price rises to the point you have set, your sell order will be activated.
The buy limit, buy stop, sell limit, and sell stop are generally referred to as pending orders.
Take Profit: It literally means what the name suggests. It is that price you set for your broker to close your trades and lock in your profits. The order is usually executed automatically on the trading platform. You can also execute it manually.
Stop Loss: If a trade goes against you, you are losing money. There is a limit to losses that you can take as a trader. This is why the stop-loss order is important. It is that price you set for your broker to close your trade to reduce losses. It can be executed automatically or manually.
There is an advanced form of the stop loss order called the guaranteed stop loss order (GSLO). This order makes sure that your stop loss order is executed at the exact price you choose so you don’t lose more money. That is, your stop loss order is not subjected to slippage. A premium fee is usually charged for GSLO. Though it is not offered by all brokers, GSLO can be very key to your risk management strategy.
Trailing Stop: The trailing stop is similar to the stop loss because it automatically closes your trade if price movement is unfavorable. Also, it does this within a specified distance. But they differ in one crucial way.
When price moves in your favor, it moves the trailing stop along with it. Trailing stop allows you to capitalize on favorable market movement while managing your risk effectively.
14) Copy Trading: Not all traders have the time to sit with charts, analyze, and place trades. For such traders, copy trading is very essential. It is a way of trading that allows you to replicate the trades of successful traders in your account. This can be automated or executed manually.
15) Expert Advisors: Also known as EAs, expert advisors are programmed trading bots that run on trading platforms. They analyze the market according to the conditions and parameters you set in them. Based on this analysis, they can suggest a trade for you or place a trade automatically.
How to Start Forex Trading
Here is a step-by-step guide that will help you start your forex trading experience.
1) Education: It is essential you learn the basics of forex trading. You need to know about currency pairs, exchange rate, and some the definition of a number of terms. You also need to know how the forex market operates plus fundamental and technical analysis.
2) Understand Risk: Forex trading is risky. More than 70% of retail forex traders lose their money when trading. You must understand that you will be trading with leverage which can lead to total loss of your trading capital.
3) Choose a Broker: You should research and choose a reliable broker. You should compare different brokers based on factors such as regulation, trading fees, customer support, etc. Ensure the Financial Sector Conduct Authority (FSCA) regulates any broker you choose.
4) Trading Plan: You need to create a concise trading plan. It should contain your trading strategy, goals, and risk appetite. This is essential for you to remain disciplined in trading.
5) Trading Strategy: Choose the trading strategy you want to employ. Do you want to scalp? Do you prefer day trading? You might even prefer swing trading. Your trading strategy should also include your entry and exit conditions. This will help you avoid random trading.
6) Open a Demo Account: A demo account is a practice account. It allows you to test your trading strategy without risk of losing money. Your broker will give you virtual money that you can trade in a simulated environment. You will be familiarized with the market and your trading platform.
How to Open Forex Trading Account
To open a forex trading account, you need to first choose a reputed broker that is regulated by the FSCA. There are many brokers regulated in South Africa, so you should compare forex brokers by checking their regulation and safety of funds, trading, and non-trading fees, trading application platforms supported, instruments available for trading, customer support, ease of deposits/withdrawals, etc.
After you have researched and decided on the forex broker that you want to trade with, you should open your trading account. We will take HF Markets (HotForex) as an example. The steps involved are generally the same for all forex brokers.
To start trading forex in South Africa, follow the steps below to create a live trading account.
Step 1) Go to the HF Markets website at www.hfm.com and click on the ‘Open Live Account’ button, highlighted in green colour, at the top right side of the page.
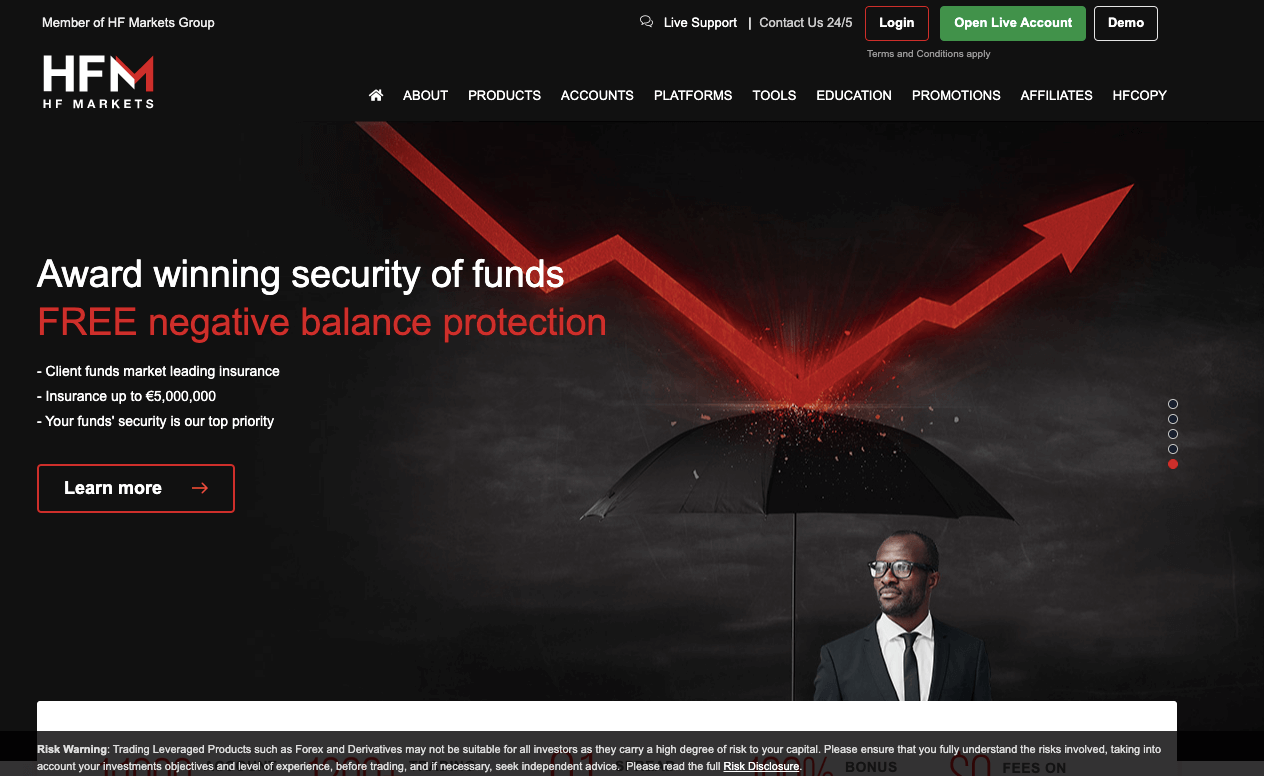
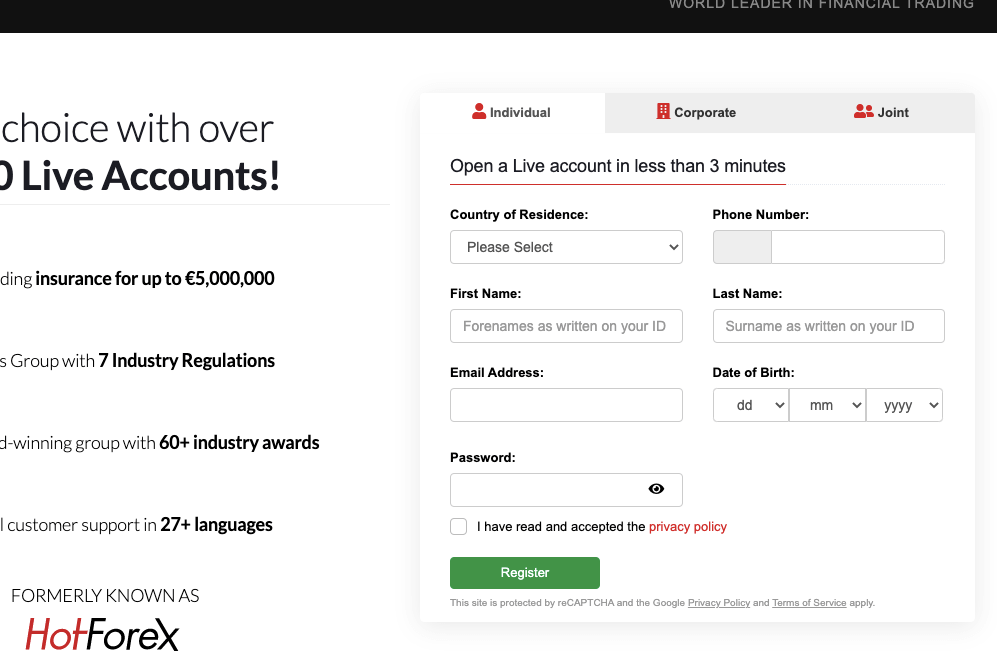
Step 2) Select the client type, either as an individual, corporate or joint, then fill in your information, create a password, select South Africa as your country of residence, check the terms and conditions box after reading, and click on ‘Register’.
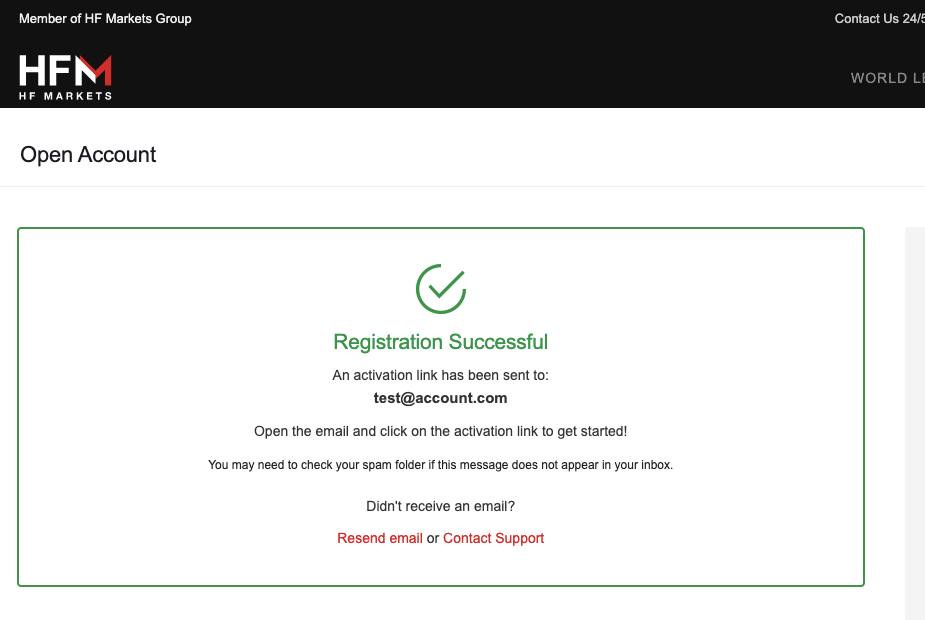
Step 3) A verification link will be sent to your email address. Go to your email inbox and click the ‘Activate Account’ link to continue with your registration.

Step 4) When you click on ‘Activate Account’ in the email, your account will be activated, and you will be taken to your dashboard (an example is shown below).
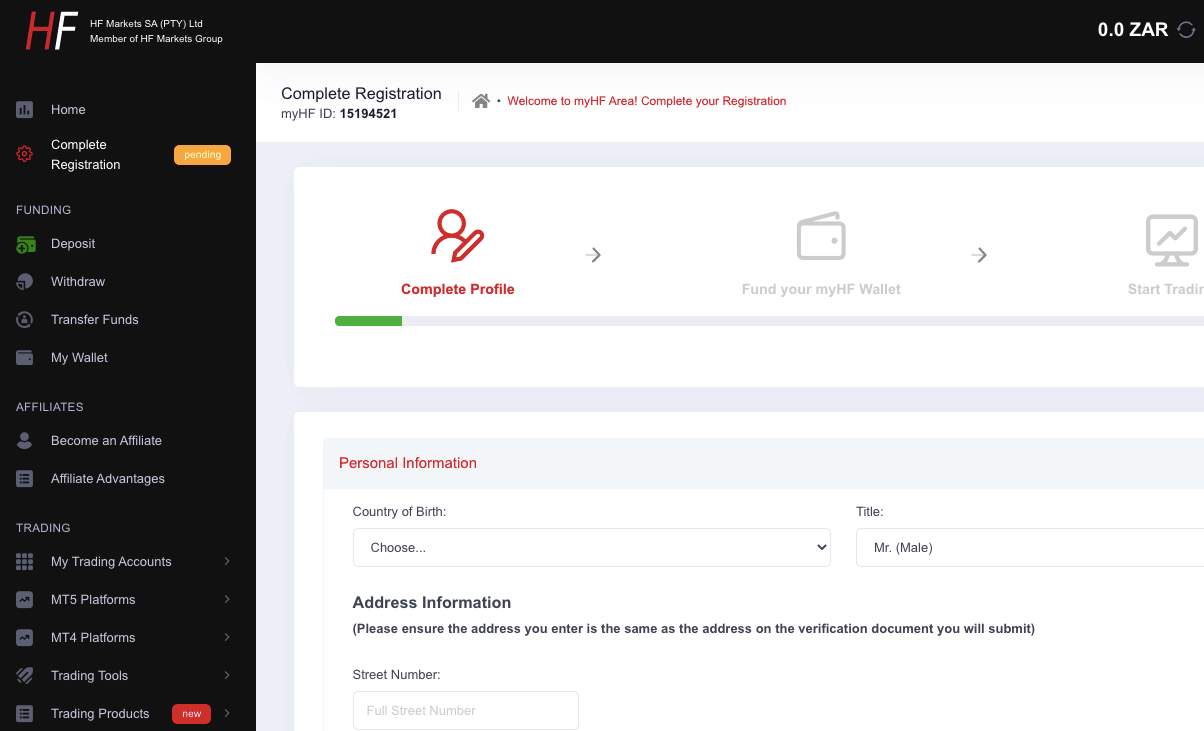
You will also get a confirmation email with your ‘myHF account ID’ after the account is activated.
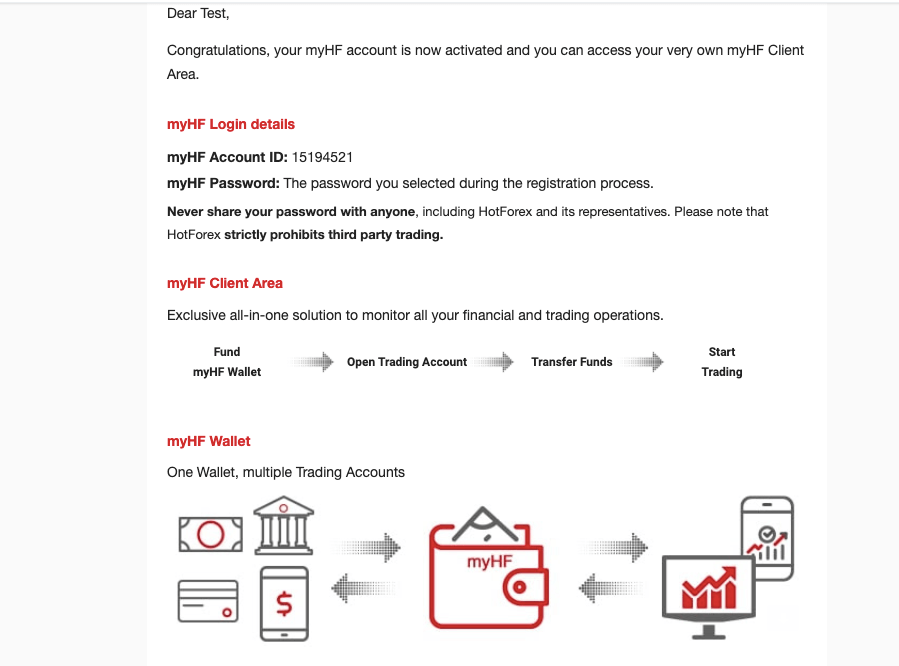
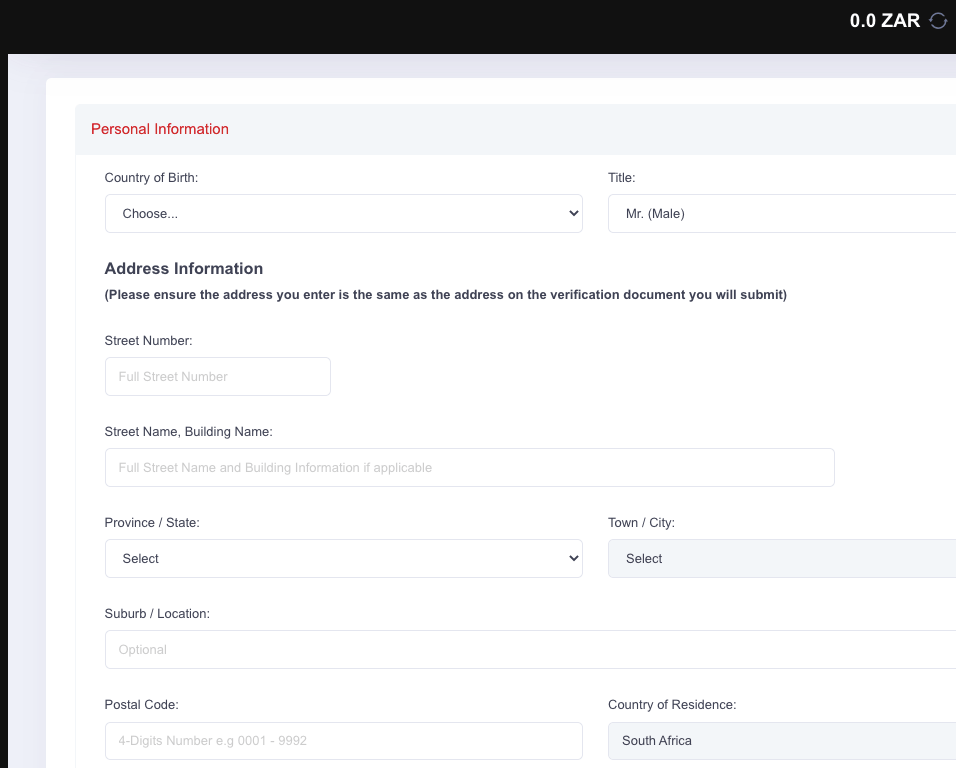
Step 5) On your dashboard, you will be required to complete registration/profile by supplying some personal and economic information, including your experience level with Forex trading.
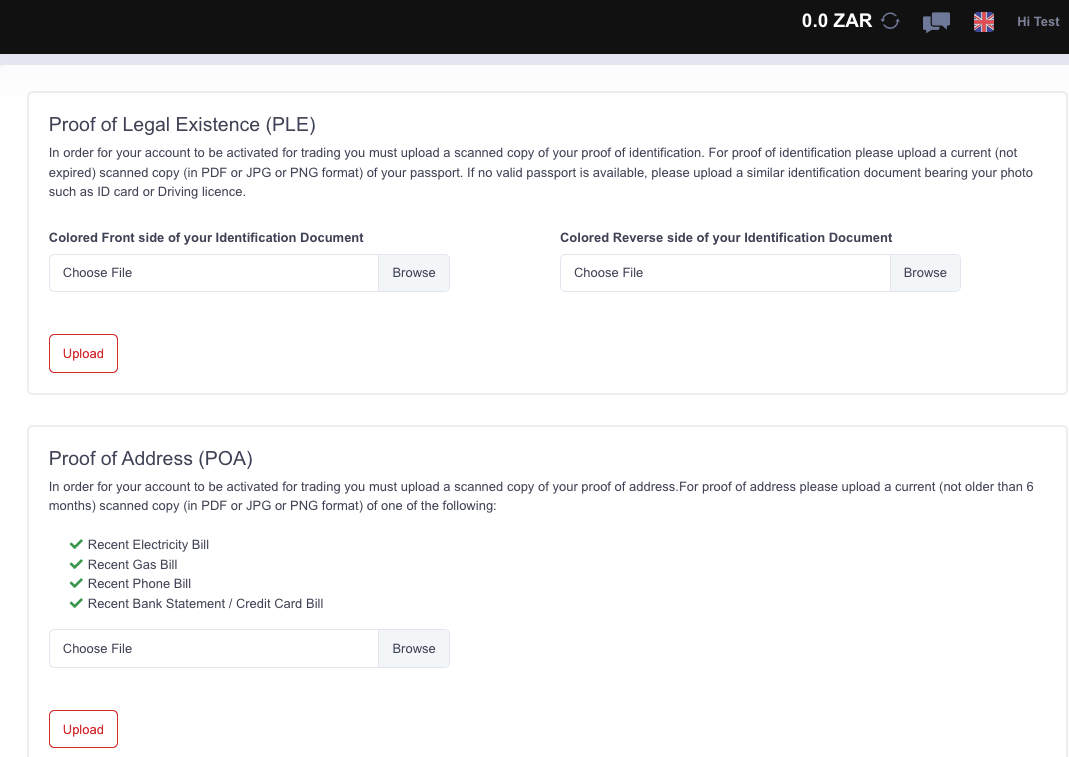
Step 6) Next, you will be required to upload a valid ID to verify your identity and a proof of address to verify your address. Then wait for the approval.
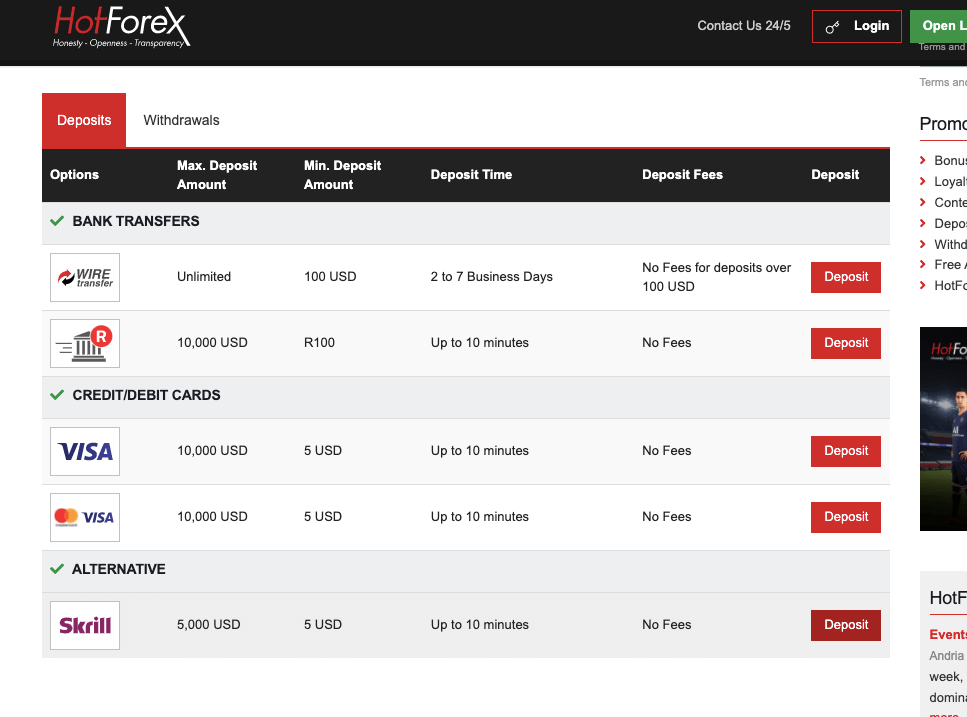
After your account is approved, you can make deposits, start trading, make transfers and withdrawals.
tep 7) Download the Platform: All brokers offer platforms like MetaTrader or their own proprietary platforms. Most forex brokers offer multiple platforms.
You will generally get an email from the broker regarding the details on how to download and log in to your platform.
Step 8) Deposit Funds: You can choose methods like a card or bank transfer for depositing. Watch out for brokers that charge extra fees during deposits.
Also, avoid any brokers that charge excessive withdrawal fees. Some brokers claim to charge low trading fees, while charging excessive charges on withdrawals & deposits, making their overall fees very high.
What are Forex Trading Platforms?
Forex brokers act as intermediaries between traders and the market. When you open a trading account, you will need a platform to analyze CFDs, and place and monitor your trades. These platforms are offered by CFD brokers and they are divided into two categories. They are ‘third-party’ and ‘proprietary’ platforms. A forex broker can have both or one of the categories.
Third-party platforms are trading apps or software developed by another company. Forex brokers partner with these companies to develop these platforms for them. A common example of these is MetaTrader 4, MetaTrader 5, and cTrader. These three are the most popular trading platforms. They are available on mobile phones, desktops, and web-based trading platforms. You can download them from your broker’s website. The mobile versions are available on Google Play Store and App Store.
In addition, there are third-party platforms that allow forex brokers to link their client’s accounts to their own platforms. TradingView is a typical and common example of this kind of platform.
Proprietary platforms are the opposite of third party platforms.They are owned and developed by individual forex brokers. Some forex brokers prefer to develop their own apps and software for traders. They can be available on mobile, desktop, or on the web. eToro, for example, does not have any third-party platforms. They only offer their CFD trading platform and Copytrader.
Risks Involved in Forex Trading
The forex market is very liquid and this liquidity has caused a lot of traders to throw caution to the wind and even become greedy.
Most retail traders trade forex because of leverage, and this can cause losses to escalate very quickly.
Let us discuss some risks.
1) Risk of Unlicensed Forex Brokers
There are lots of unlicensed brokers who lure unsuspecting traders with promises of huge returns with low investments.
Some of them claim to hold licenses from regulators in countries that are not known for strong regulatory supervision.
Forex traders in South Africa must only trade via FSCA-licensed forex brokers. Traders should go to the FSCA website at ‘www.fsca.co.za/fais/search_fsp.htm’ and check if their broker is on the list of licensed forex brokers.
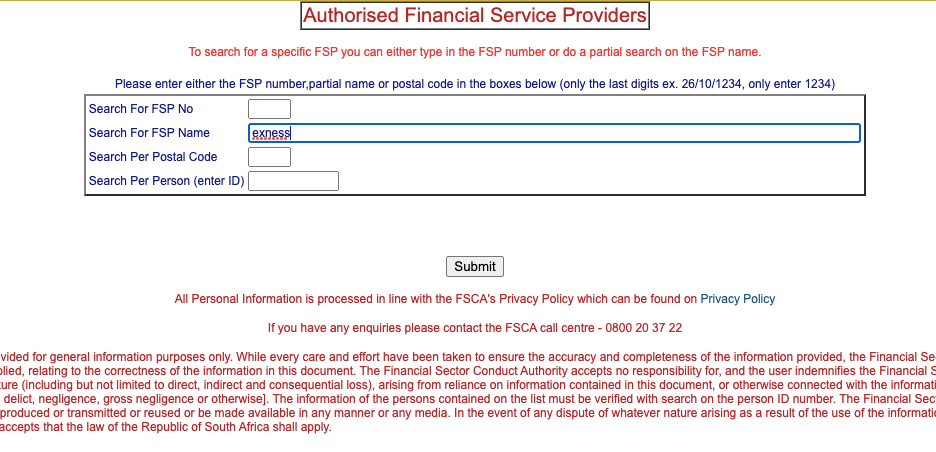
Each forex broker in South Africa is issued a unique FSP (Financial Services Provider) number which would aid your verification of the broker’s authenticity. In the screenshot below a forex broker – Exness – has an FSP number 51024 which is used to search on the FSCA website to produce one match.
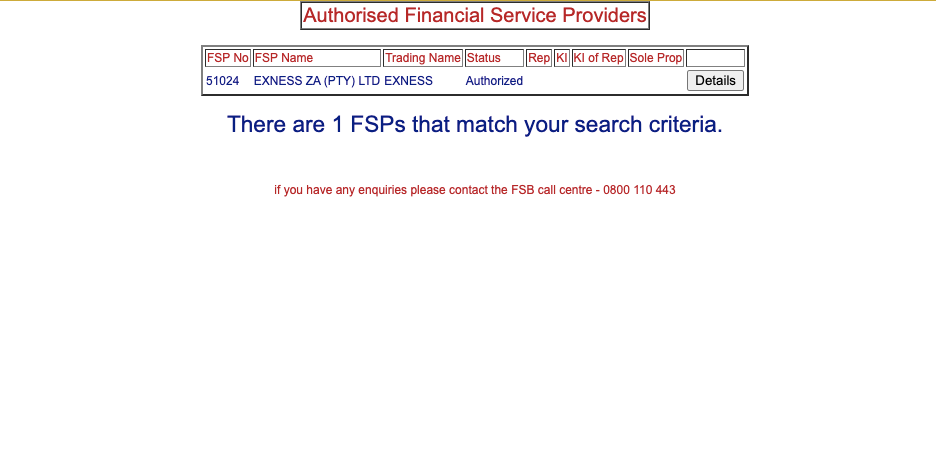
While at it you can click on ‘Details’ to check the phone number of the broker when it was licensed, the approved products list and other relevant details. You can call the broker’s phone number on the FSCA website related to the forex broker and call the number to be sure you are dealing with a legitimate broker.
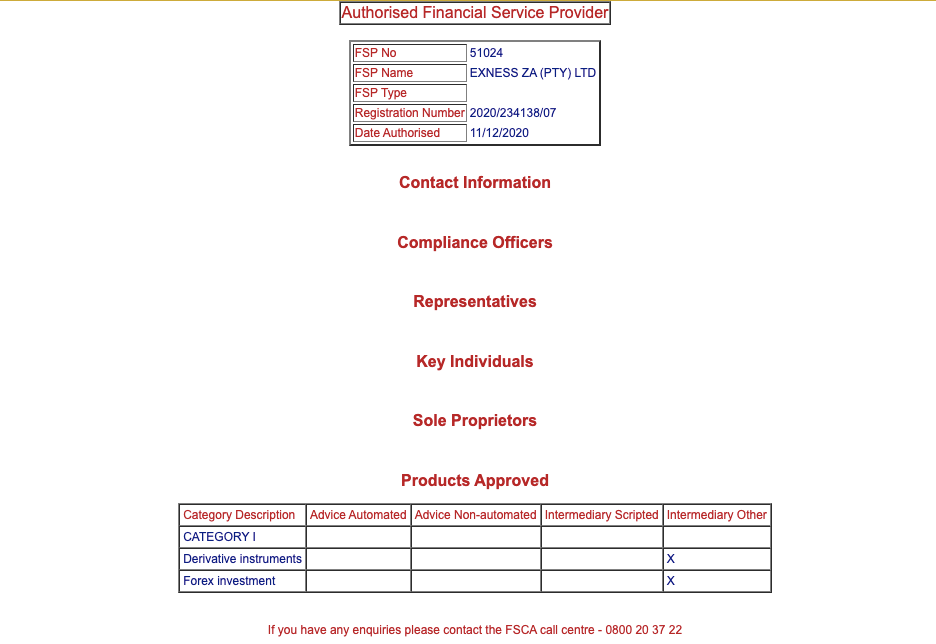
Finally, you need to make sure you are not exposed to too much risk. You should do this even if your broker is regulated with the FSCA. This is crucial because the FSCA is not a tier-1 regulatory body. So you should make sure any broker you choose is regulated with the FSCA and a tier-1 regulator.
The United Kingdom’s Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) and the Australian Securities and Investments Commission (ASIC) are recognized tier-1 regulators. An FSCA license combined with FCA or ASIC license makes a broker significantly low risk.
2) Risk of Cloned Forex Brokers
Some scam forex brokers go ahead and clone other licensed brokers.
They go as far as hosting websites with logos and registration numbers to deceive unsuspecting targets. Forex traders must be watchful and look out for red flags such as little differences in the broker name. Forex traders should also report any cloned page they come across to the FSCA.
Scam brokers do exist so you should be wary of them and report anyone you come across to the FSCA.
The first two risks that we discussed are associated with the risk due to a third party i.e. your broker. We will now talk about the risks that you face with actual trading.
3) Leverage risk
Forex brokers in South Africa can offer leverage as high as 1:1000 to their clients
This being said, forex traders should resist the urge to open an account with brokers outside South Africa who offer higher leverage.
Reports state that even with the leverage restrictions, 70 to 80% of retail forex traders lose money. The actual percentage depends on the broker to broker.
This is mainly because of over-leveraging a position. Traders must avoid using more than 1:10 leverage on any forex trade.
Let’s take an example, let’s say you place a buy order on EUR/USD at 1.1000 targeting 1.1100, which is 100 pips. You have $10,000 in your trading account & you decide to use 1:10 leverage to place 1 Standard lot trade.
If the price does go in your direction, then you can make a profit of $1000 on this trade. But if the price goes against you by let’s say 100 pips, then you would lose $1000, which is 10% of your capital. If you had used 1:30 leverage, then the losses would have been $3000, which is 30% of your capital on a single trade.
Hence, you must remember that trading with excessive leverage can cause big losses.
The use of leverage should be done responsibly as it amplifies both gains and losses. You should find out if your broker offers negative balance protection so as to stop your account from going into negative.
You can also use Stop Loss orders to automatically exit a position if the loss exceeds a certain level. Stop-loss orders are automated instructions a trader gives the broker to exit his trading position once the price goes below a predetermined amount. Stop-loss orders could be used to manage risk.
4) Risk of Losses from your trades
The forex market is very volatile and should be approached with caution. For example, it is not uncommon for some currency pairs to move 4-5% in a day.
Normally, even majors like EUR/USD can move 1-2% in a single day. If you are risking too much on a single trade, then you can lose very quickly.
In fact, most of the retail traders trading in the forex market lose their money. It is really hard to be profitable with forex trading, mostly because traders trade with gamblers’ nature of risking excessively.
It is really important to practice risk management on a demo account for some months before going live. Also do not risk more than 2% of your trading capital on one trade.
Types of Analysis in Forex Trading
In the world of forex trading, there are two major types of analysis — fundamental and technical analysis. Technical analysis focuses on price patterns (present and historical), indicators, use of drawing tools, etc. On the other hand, fundamental analysis has to so with how political and economic factors affect the value of currencies.
In this section, we will be breaking down both methods to help you understand them better.
1. Fundamental Analysis: The health of an economy is crucial to the strength of its currency. The aim of fundamental analysis is to determine how the health of an economy affects the value of its currency. There are different components of fundamental analysis that can help you determine the direction of price for a currency pair.
Here are some of them.
Economic indicators and releases: Economic indicators are quantitative and objective. They usually have a numerical value that helps to determine the strength of a currency. Examples include GDP, interest rate, unemployment rate, non-farm payroll, etc.
Economic releases are qualitative and their interpretations can be subjective. Examples include a speech from the President of the ECB.
Geopolitical Events: Diplomatic tensions, wars, trade disputes, and policy changes can affect the value of a currency. Fundamental analysis considers these factors and their potential impact on a country’s economy and currency.
Political Stability: A country with a stable political atmosphere will mostly have a strong currency. Furthermore, stable politics in a country attracts investors. Increase in investors will lead to an increase in the demand for a country’s currency, making it stronger in the process.
You can find the data you need for fundamental analysis. But most forex brokers have them on their websites or third-party trading platforms. It is usually called the Economic Calendar.
It is important to note that economic analysis requires a deep knowledge and understanding of economic concepts. You also have to monitor global events consistently. It takes time for economic factors to affect the price of currency pairs. So if you prefer fundamental analysis, you need to be patient and have a long-term perspective.
2. Technical Analysis: Technical analyses is used to predict the future prices of different CFDs. Traders who prefer this method depend on historical prices, chart patterns, and indicators to make knowledgeable decisions.
FAQs on Forex Trading in South Africa
Is forex trading Legal in South Africa?
Yes, Forex trading in South Africa is legal for retail traders & it is regulated by the FSCA. For ensuring that your funds are safe with the broker, you must only trade via regulated brokers.
Is forex trading good for beginners?
Forex trading involves a lot of risks and inexperienced people can lose all their money. Beginners who are new traders are advised to first create a demo account and practice trading with virtual money before putting in their real money.
As reported by major regulators, as high as 85% of traders lose at retail CFD brokers. So you must understand that there is no certainty of profits.
It is also best and safest to trade with a broker regulated in South Africa, that offers negative balance protection and requires little deposit. As a beginner, you should also not use high leverage as it will increase your risk and potential losses.
Do forex traders pay taxes in South Africa?
Yes, South African traders are required to pay income tax on profits generated from forex trading. This rule applies to offshore forex trading accounts too.
How do I start my forex trading?
To start forex trading in South Africa, first compare the many forex brokers that are regulated in South Africa, then open a live trading account with your preferred broker. Next step is to download their trading platform, make deposits and start trading. You may need to watch some educational videos on using the trading platform. You can find such videos on the forex brokers website.
What is forex trading and how it works?
Forex trading involves buying and selling currency pairs like EUR/USD, GBP/USD, EUR/GBP etc. A forex trader speculates on the prices of currencies. For example, if a trader thinks that the USD is going to be weaker in the next few weeks against the GBP, then that trader can buy GBP, that is the GBP/USD pair.
If the trader is right and the USD becomes weaker, the trader makes profits from the difference. Forex trading generally involves leverage, which is very risky as we explained in our guide.
How much money do you need to start trading forex in South Africa?
The amount of capital that you put totally depends on your risk level. Most brokers allow low deposits. For example, HF Markets has a minimum deposit of R100 or $5. Depending on how much risk you want to take, you can decide the amount. But it is really important to never trade with capital that you cannot afford to lose as the probability of losses for retail traders are very high. Have a strategy to manage your risks.
























